Stable gene expression for normalisation and single-sample scoring
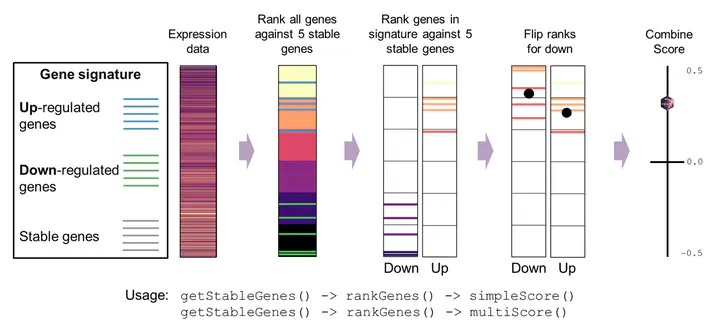 Schematic of stingscore (singscore with stably expressed genes)
Schematic of stingscore (singscore with stably expressed genes)Abstract
Gene expression signatures have been critical in defining the molecular phenotypes of cells, tissues, and patient samples. Their most notable and widespread clinical application is stratification of breast cancer patients into molecular (PAM50) subtypes. The cost and relatively large amounts of fresh starting material required for whole-transcriptome sequencing has limited clinical application of thousands of existing gene signatures captured in repositories such as the Molecular Signature Database. We identified genes with stable expression across a range of abundances, and with a preserved relative ordering across thousands of samples, allowing signature scoring and supporting general data normalisation for transcriptomic data. Our new method, stingscore, quantifies and summarises relative expression levels of signature genes from individual samples through the inclusion of these ‘stably-expressed genes’. We show that our list of stable genes has better stability across cancer and normal tissue data than previously proposed gene sets. Additionally, we show that signature scores computed from targeted transcript measurements using stingscore can predict docetaxel response in breast cancer patients. This new approach to gene expression signature analysis will facilitate the development of panel-type tests for gene expression signatures, thus supporting clinical translation of the powerful insights gained from cancer transcriptomic studies.